Lesson 17: Master-Slave Replication
Scaling Twitter's Database for 1,000 Concurrent Users
Video:
What We're Building Today
Today we're implementing Master-Slave Database Replication - the backbone that lets Twitter handle millions of reads while maintaining data consistency. You'll build a replicated database system that automatically distributes read queries across multiple slave databases while routing all writes to a single master.
Key Deliverables:
Master-slave PostgreSQL replication setup
Smart connection routing between master/slave databases
Automatic failover handling for 99.9% availability
Real-time replication lag monitoring dashboard
Why Master-Slave Replication Matters
Think about Twitter during breaking news - millions of users refreshing their timelines simultaneously. Without replication, your single database becomes the bottleneck that crashes your entire system. Master-slave replication solves this by creating multiple read-only copies of your data.
Real-world Impact: Instagram uses master-slave replication to handle 95% of their database traffic through read replicas, reducing response times from 200ms to 50ms for timeline queries.
Core Concepts
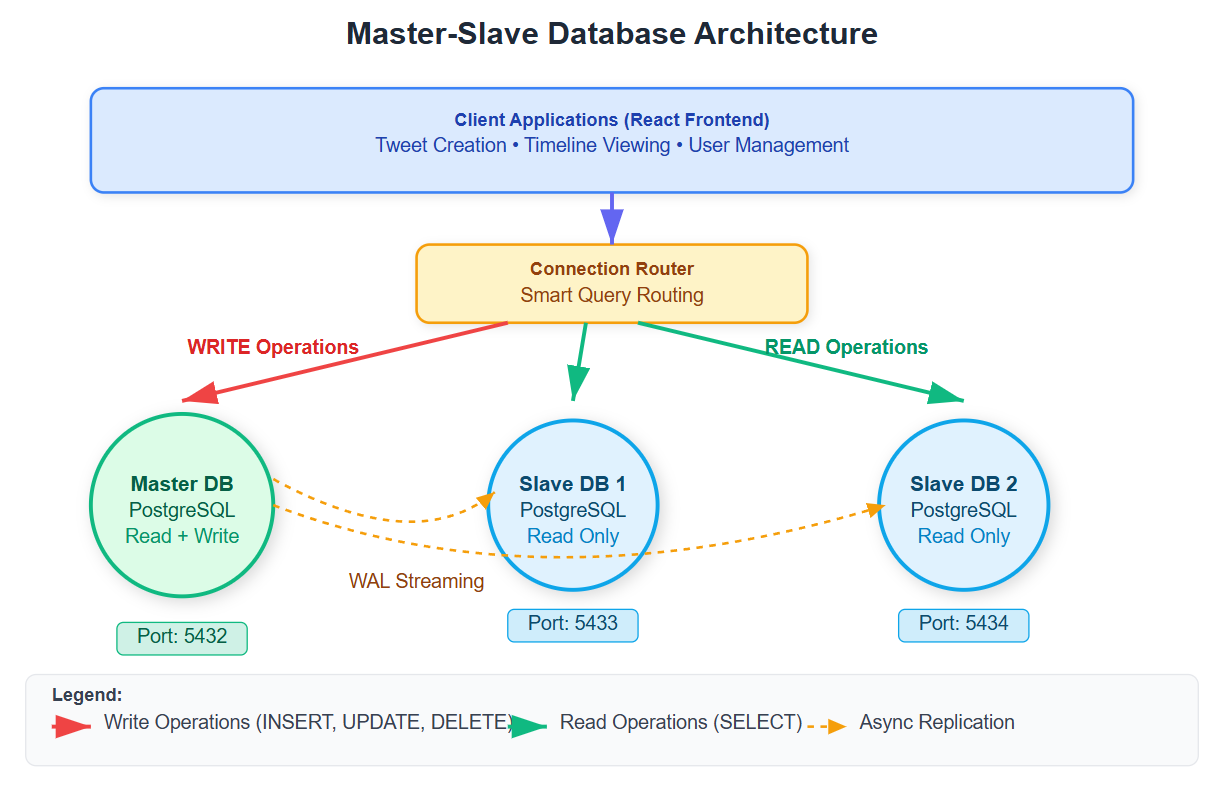
Master-Slave Architecture Pattern
The master database handles all write operations (tweets, follows, likes) while slave databases serve read requests (timeline generation, user profiles). This separation allows horizontal scaling of read capacity without affecting write performance.
Replication Workflow:
User posts tweet → Application writes to Master DB
Master DB automatically replicates data to Slave DBs
Timeline requests → Application reads from Slave DBs
Write operations → Application always uses Master DB
Consistency Challenges: Replication lag means slave databases might be 50-200ms behind the master. Your application must handle scenarios where a user posts a tweet but doesn't see it immediately in their timeline.